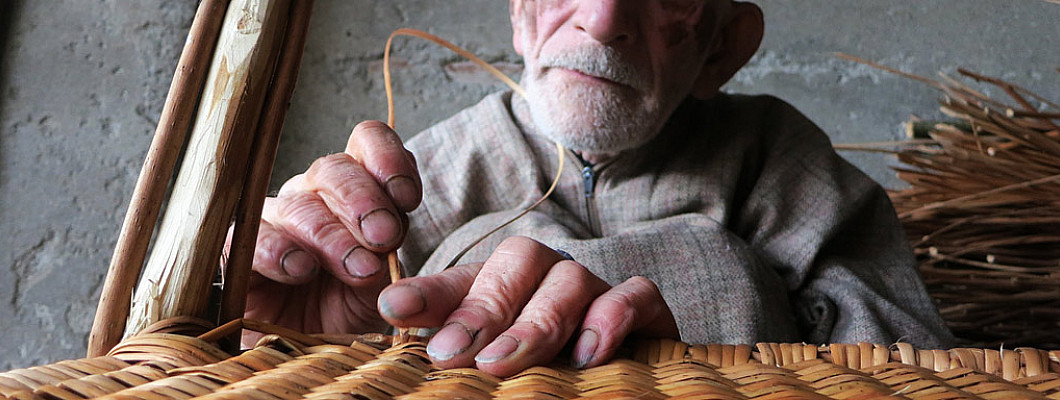

Who comes first- craft or craftsmen?
Its very difficult to define, one thing is very clear that in our evolution after mind hands play a significant role, from making tools to farming they are the exual stack holder. In indian culture the position of the craftsmen are always valuable. Manu says- “the hand of a craftsman engaged in his craft is always pure”. In old time every region was sustainable, The craftsmen working within the village community, are there in virtue of a perpetual contract whereby their services are given to the village or community, from whom they receive in return certain privileges and payments in kind. Each has his own duties to perform.
The woodwork of ploughs and other implements is made and repaired by the carpenter, the cultivator merely supplying the wood; the blacksmith supplies all the iron parts of the implements, and repairs them when necessary, the cultivator supplying the iron and charcoal, and working the bellows; and the potters supplies each cultivator with earthenwear they needs.
If we see the definition of handicrafts of India, it may say- products made entirely by hand or with minimal mechanical assistance, ensuring each piece maintains uniqueness and reflects the artisan’s creativity. But again it’s a very material approach, it dosent talk about the mind, need, material and surrounding. Accouding to definition food we cook in india everyday is also a handicrafts? why not our traditional cooks are also artisans they keep traditional recipecy alive and maintaining the uniqueness of that specific food alive.

Handicrafts meaning/ Defination, Handicrafts vs handmade
The act through which any object is crafted or made by hand or with simple tools is called handicraft. Handicrafts traditional, skill-based crafts created by artisans using hand tools or minimal machinery. These crafts often carry cultural and historical significance. but Handmade could be Any product made by hand, regardless of skill level, cultural significance, or tradition. This term has a broader application and can include anything from DIY projects to professionally crafted goods.If we see the meaning of the word handicrafts in hindi it says hastashilp. hasta meaning hand and shilp meaning art. if we this as todays approach, we are calling it design. when we do things with perpose it’s a design and art is more subject to the artist. So craftsmen who are making things are actually a designer or artist? They are the terms of discussion and dose not hold any significance. What we know is artisans are the knowledge holder and making our life better and pleasant.

History of Indian Handicrafts
History of handicrsft are as old as human civilization, old wall art in differebt cave represent the expression from a artist, different handmade stone tools says about their understanding about the material. With the time they have evolved by passing knowledge to younger generation and by the time of Indus Valley Civilization we can see the advance version of handicrafts, where artisans crafted pottery, textiles, and jewelry with remarkable finesse. Later Over centuries, various dynasties enriched this tradition—the Mauryan and Gupta empires fostered sculpture and textile arts, while the Mughal era introduced intricate inlay work and miniature painting. Each period added layers of sophistication, shaping India’s distinctive artistic heritage.
Colonial rule and industrialization posed challenges to traditional crafts, yet the late 20th century saw a revival. Today, renewed appreciation for handmade artistry has rekindled interest in indigenous crafts, blending tradition with modern sensibilities. This evolution is not just a historical record—it is a continuing narrative of resilience, adaptation, and enduring beauty.

Cultural Significance and Economic Impact
Indian handicrafts is second largest economy after agriculture, it create direct and indirect opportunity of million of peoples. Beyond cultural preservation, handicrafts play a crucial role in economic empowerment, particularly in rural India. Artisan communities rely on their craft for sustenance, and increasing consumer interest in handmade goods has fueled market opportunities. Ethical consumerism and sustainability movements have further elevated the status of Indian handicrafts, positioning them as symbols of mindful living and heritage conservation.

The Indian Artisans: Keepers of Tradition
At the heart of Indian handicrafts are the artisans, men and women who dedicate their lives to mastering and preserving their craft. Many hail from families that have practiced the same art form for generations, learning techniques through an informal yet rigorous apprenticeship. Their skill, patience, and innovation ensure that these art forms remain vibrant and relevant.
However, artisans face challenges such as market accessibility, competition from mass-produced goods, and economic instability. Initiatives promoting fair trade, skill development, and digital platforms are instrumental in sustaining these crafts and ensuring that artisans receive fair compensation for their work. By supporting handmade products, consumers contribute directly to the survival and flourishing of India’s artisanal heritage.

Promoting and Preserving Indian Handicrafts
The survival of Indian handicrafts depends on active promotion and preservation. Government initiatives, NGOs, and private enterprises play a crucial role in empowering artisans through market access, training, and financial support. Initiatives like the Geographical Indications (GI) tag help protect traditional crafts, ensuring authenticity and recognition.
Digital marketplaces and social media have revolutionized the way artisans connect with global audiences. Online platforms enable direct-to-consumer sales, allowing artisans to expand their reach beyond local markets. Collaborations with designers and brands have also modernized traditional crafts, making them relevant to contemporary aesthetics while preserving their essence.
Educational efforts to integrate traditional crafts into school curricula and community programs are essential to ensuring that younger generations appreciate and carry forward these traditions. By fostering awareness and appreciation, we can safeguard the future of Indian handicrafts.
Social media has played a significant role in this growing appreciation, allowing artisans to showcase their work and connect with buyers across the globe. This digital renaissance has empowered craftsmen, making Indian handicrafts more accessible and desirable on the world stage.

The Diversity of Indian Handicrafts
It is challenging to capture the vast diversity of Indian handicrafts. If you take a simple material and travel across different region, you will find unique forms and functions shaped by local traditions and resources. Before communication revolution they are the people who use to apply their creativity and skills to make something unique and later that style become their identity. From Kashmir’s luxurious Pashmina shawls to Tamil Nadu’s opulent Kanchipuram sarees, every craft reflects the traditions and natural resources of its origin. Rajasthan’s intricate blue pottery, Gujarat’s vibrant Bandhani textiles, and the Northeast’s bamboo and cane crafts exemplify the depth of India’s artistic landscape.
Though it is difficult to define an exhaustive list of Indian handicrafts, here are some famous crafts from different states. These lists provide a glimpse into the rich handicraft traditions of each region but do not encompass their full diversity.
indian handicrafts chart | State-wise list of Indian handicrafts
Handicrafts of Jammu & Kashmir – Pashmina Shawls, Papier-Mâché, Carpet Weaving, Walnut Wood Carving
Handicrafts of Himachal Pradesh – Kullu & Kinnauri Shawls, Chamba Rumal, Metal Crafts, Wooden Toys
Handicrafts of Punjab – Phulkari Embroidery, Jutti (Footwear), Wood Inlay Work
Handicrafts of Haryana – Surajkund Terracotta, Shawl Weaving, Wood & Ivory Carving
Handicrafts of Uttarakhand – Aipan Art, Ringal Craft, Copperware, Woolen Shawls
Handicrafts of Delhi – Meenakari Work, Zardozi Embroidery, Silver Filigree
Handicrafts of Rajasthan – Blue Pottery, Block Printing, Meenakari, Kathputli (Puppetry), Leatherwork
Handicrafts of Gujarat – Bandhani (Tie & Dye), Patola Sarees, Rogan Painting, Kutch Embroidery, Wood Carving
Handicrafts of Maharashtra – Paithani Sarees, Bidriware, Warli Painting, Kolhapuri Chappals, Sawantwadi Lacquerware
Handicrafts of Goa – Azulejos Tiles, Crochet & Embroidery, Sea Shell Craft, Wooden Carving
Handicrafts of Madhya Pradesh – Chanderi & Maheshwari Sarees, Gond Painting, Dhokra Metal Craft, Zari Work
Handicrafts of Chhattisgarh – Bastar Dhokra, Tumba Art, Godna Art, Kosa Silk
Handicrafts of West Bengal – Kantha Embroidery, Baluchari Sarees, Sholapith Craft, Terracotta Work
Handicrafts of Odisha – Pattachitra Painting, Silver Filigree (Tarakasi), Sambalpuri Ikat, Applique Work (Pipili)
Handicrafts of Bihar – Madhubani Painting, Sujni Embroidery, Sikki Grass Craft, Tikuli Art
Handicrafts of Jharkhand – Sohrai & Khovar Painting, Dokra Metal Craft, Terracotta Art
Handicrafts of Assam – Muga Silk, Assamese Gamusa, Bell Metal Craft, Bamboo & Cane Work
Handicrafts of Meghalaya – Weaving of Eri Silk, Bamboo Crafts, Wood Carving
Handicrafts of Manipur – Manipuri Handloom, Kauna Grass Craft, Black Pottery
Handicrafts of Nagaland – Naga Shawls, Cane & Bamboo Work, Wood Carving
Handicrafts of Arunachal Pradesh – Thangka Painting, Carpet Weaving, Cane & Bamboo Craft
Handicrafts of Mizoram – Puan Fabric Weaving, Bamboo & Cane Handicrafts
Handicrafts of Tripura – Risa Handloom, Bamboo Work, Tribal Jewelry
Handicrafts of Sikkim – Thangka Painting, Carpet Weaving, Wood & Metal Craft
Handicrafts of Tamil Nadu – Kanchipuram Silk Sarees, Tanjore Painting, Bronze Sculpting, Toda Embroidery
Handicrafts of Kerala – Kathakali Mask Making, Aranmula Mirror, Nettipattam (Elephant Caparison)
Handicrafts of Karnataka – Mysore Silk, Channapatna Toys, Bidriware, Sandalwood Carving
Handicrafts of Andhra Pradesh – Kalamkari Painting, Etikoppaka Toys, Kondapalli Wooden Toys
Handicrafts of Telangana – Pochampally Ikat, Pembarthi Brassware, Nirmal Painting
With a diverse landscape and rich cultural heritage, each region showcases its unique identity through its crafts. Artisans draw inspiration from folklore, mythology, and nature, ensuring that every creation carries a piece of history while remaining relevant to contemporary tastes. This regional diversity not only preserves traditional techniques but also offers a vast spectrum of artistic expressions to the world.
With growing global influence, visual culture is evolving rapidly. To preserve India's craft heritage, we need a clear and intentional approach. These crafts are not just a source of livelihood; they are a reflection of our identity and cultural legacy.









Leave a Comment